Our YouTube channel: Русский
Contracts with industry
We develop applied research in collaboration with Russian and foreign universities and industrial organizations, among which there are JSC “Russian Space Systems”, JSC “Gazprom Space Systems”, Lavochkin Research and Production Association, JSC Information Satellite Systems – Reshetnev Company, “ScanEx R&D Center”, Sputnix Ltd, Institute of Precision Instrument Engineering, JSC “NIIEM Corporation”, Makeyev State Missile Design Center (JSC “Makeyev GRTs”), FiLaS S.p.A., IRF, NSC, NSPO, TUB, Samara State Aerospace University, MIPT, Moscow Aviation Institute, UBI, ZARM. Microsatellite projects, attitude control systems of which are developed with our assistance:

The first Russian private microsatellite TabletSat-Aurora (launched in 2014), active attitude control system, 26 kg
(credit Sputnix Ltd)

The Russian microsatellite Chibis-M (launched in 2012), active attitude control system, 43 kg кг
(credit SRI of RAS)
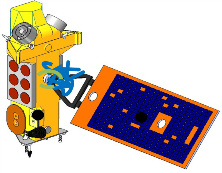
The Taiwanese satellite Formosat-7 (13), active attitude control system, 250 kg(credit NSPO)
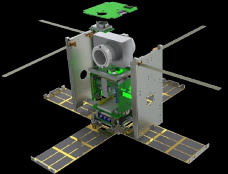
The American nanosatellite
CXBN-2, аctive attitude control system, 2.5 kg (credit Morehead State University)

The German picosatellite (cubesat) BeeSat-3
(launched in 2013), passive attitude control system with hysteresis plate, 1 kg
(credit TUB)
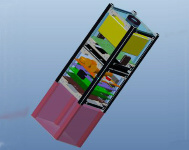
The Russian nanosatellite SamSat-QB50,aerodynamical attitude control system with hysteresis rods, 2 kg(credit Samara State Aerospace University)

The first Russian nanosatellite
ТNS-0 №1 (launched in 2005), passive magnetic attitude control system, 4.5 kg
(credit JSC “Russian Space Systems”)

The Russian nanosatellite ТNS-1, active magnetic attitude control system, self-rotation stabilization, 10 kg
(credit JSC “Russian Space Systems”)

The Italian microsatellite UniSat-4 (launched in 2004), passive magnetic attitude control system, 12 kg (credit University of Rome
“La Sapienza”)
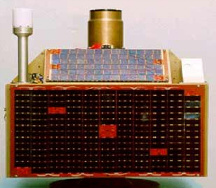
The Pakistani microsatellite BADR-B (launched in 2001), semiactive gravitational attitude control system, 70 kg
(credit SUPARCO)

The Russian nanosatellite REFLECTOR
(launched in 2001), passive gravity gradient attitude control system, 7 kg
(credit Institute of Precision Instrument Engineering)
